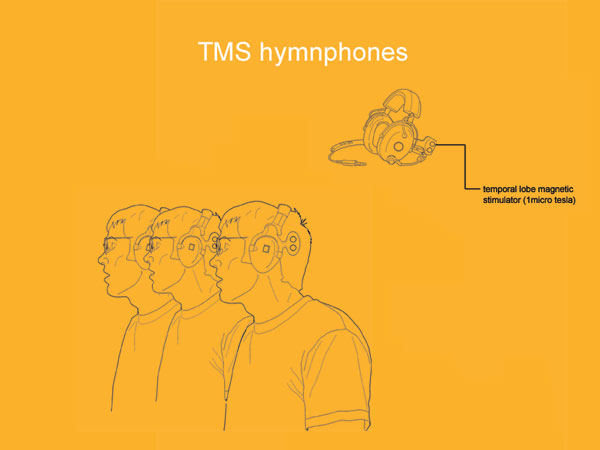
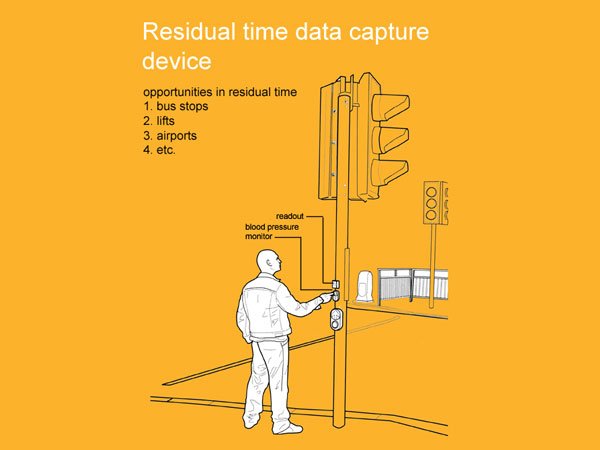
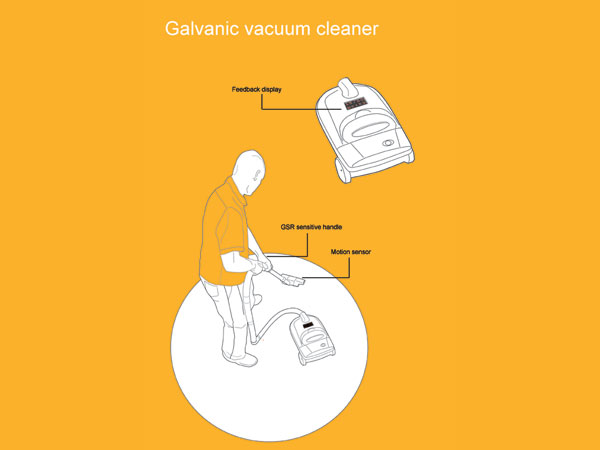
A range of experimental tools created by adding a layer of information or feedback through the surreptitious use of biometric taps. This biometric data is then used as a pointer for developing a greater understanding of ourselves and how we interact with and through products.
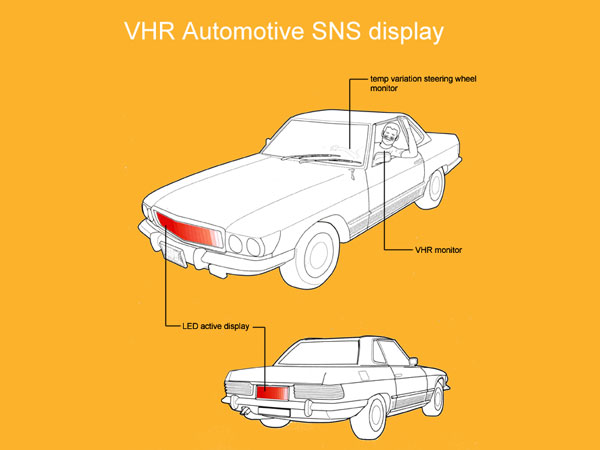
Car Display
It has been suggested that defence mechanisms triggered in stressful situations are evolutionary developments designed to increase the chances of survival.
In prehistoric times threats might have been posed by a predatory animal or by an attack from a rival tribe. In modern society similar body responses can be activated by relatively new situations such as road rage.
When the body is faced with an imminent threat, the nervous system stimulates alternative autonomic responses. These prepare the body for a suitable reaction, ‘fight or flight’ and have the effect of:
• Making the heart beat faster
• Raising blood pressure
• Dilating the pupils
• Dilating the trachea
• Stimulating the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver
• Redirecting blood away from the skin to the muscles, brain and heart
There are also visual queues such as verbal and gestured responses.
In the case of road rage, being inside the car reduces the ability of drivers to read the body language of likely aggressors and to diffuse potentially violent situations. Biometric information could play an important role in diffusing these situations. Live data, taken from the body can be incorporated into an external display showing rising stress or anger levels of the driver.
By displaying personal information regarding the status of an individual in the context of driving, how would relationships be altered? Would the driver see his levels rising and become self-conscious or embarrassed thus calming down? Would surrounding drivers acknowledge the agitated driver and give them more space?
This project explores how, by adding data to existing social scenarios or situations we can slightly alter the behaviour of the individuals involved.
How use of this technology would affect both drivers and the local geography as ‘red’ areas may become identified. How would these areas be utilized or controlled by the police or insurance companies?
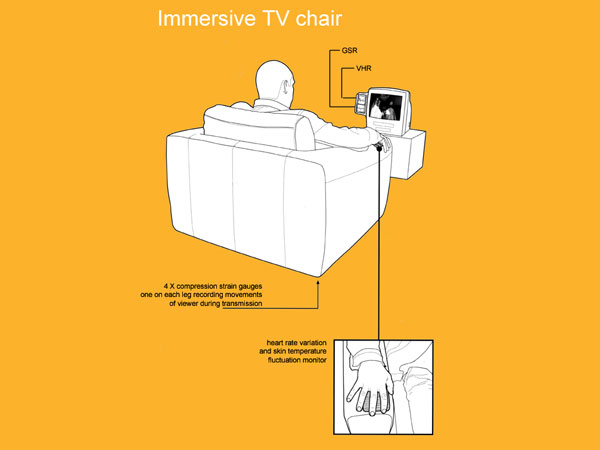
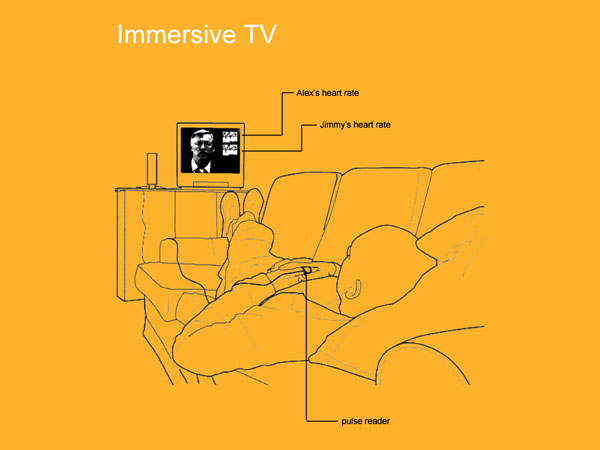
The television
“In my heart I will take my television set with me. I love you.” (Suicide note of New York schoolboy, Genero Garcia who shot himself after his father banned him from watching television)
Here we explore the enigma of television and how it has found it’s way so profoundly and intimately into the fabric of our everyday lives. Television is a medium of considerable power and significance in and for everyday life; it needs to be considered in its psychological, social and cultural form as well as an economic and political one. We will consider television as embedded in the multiple discourses of everyday life.
The impact of the television can be seen on several levels each influencing the wellbeing of the individual in differing ways.
• On a singular level: the effect on the viewer of watching a television programme or film.
• The effect at a cultural level, with the possibility for cross fertilisation and mis-representation.
• Its affect on a socio-political level on the global stage.
Television and the individual.
The complex issues surrounding the effect on the individual through watching television are worthy of contemplation. They vary from the view that television is an addictive medium, to the view of television as an inseperable companion.
The television experience allows the participant to blot out the real world and enter into a pleasurable and passive mental state. The worries and anxieties of reality are as effectively deferred by becoming absorbed in a television program as by going on a trip induced by drugs or alcohol. . We take television for granted in a similar way to how we take life for granted. We want more of it (some of us); we complain about it (but we watch it anyway) we do not understand very well (nor do we feel the need to understand) how it works, either mechanically or ideologically.
We will analyse the cause and effect of watching television on individuals, how specific genre of TV or film can change a person biometrically, and how this could affect either how we choose what we watch or how television is made.
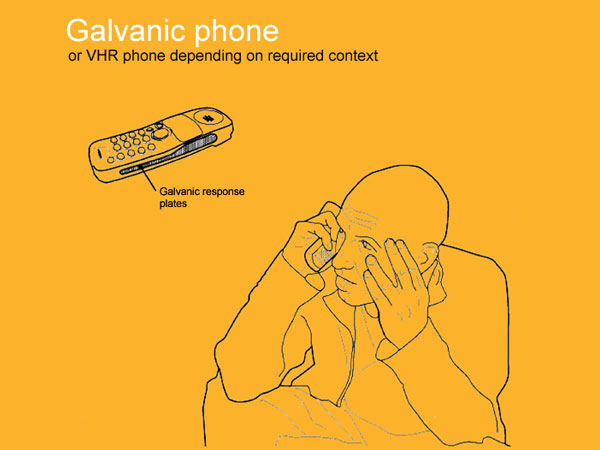
The galvanic phone.
Adds another dimension to the tele-conversation. Only becoming live when anticipation, anxiety or excitement levels reach a threshold point, the phone modifies the nature of the users behavior. Telephones no longer support meaningless or flippant conversations as the phone turns off as soon as the users levels go down. Conversations have to be pre-planned with the rigor of a parliamentary speech.
Dual activities such as watching the television whilst calling are not viable as the attention deficits caused render the galvanic phone useless.